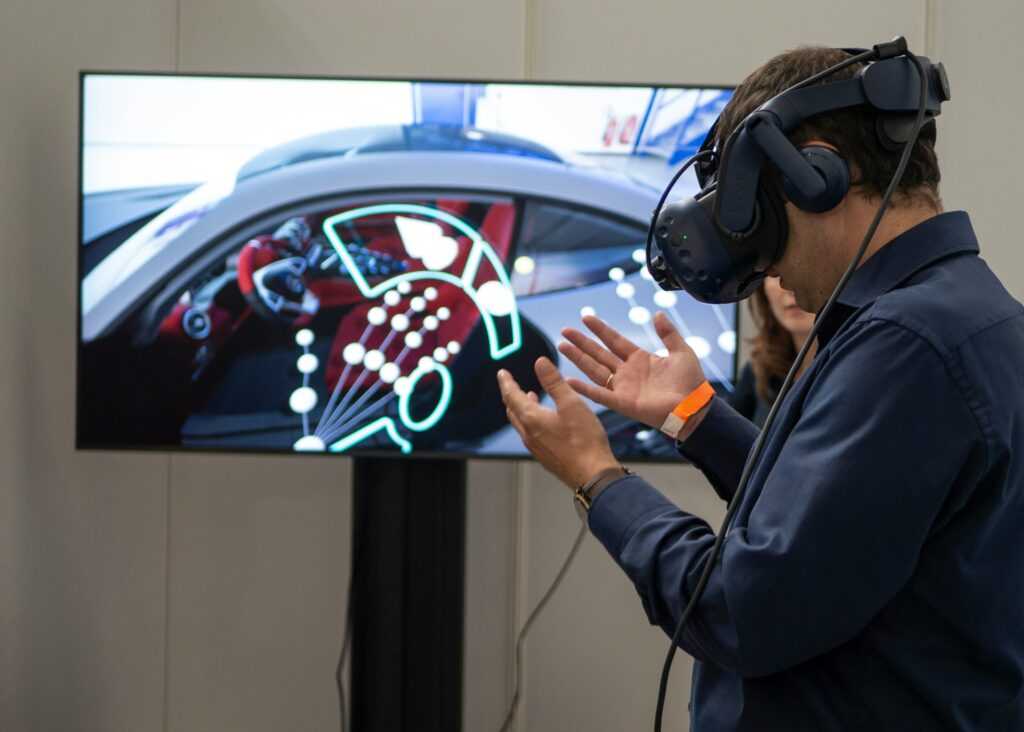
In today’s ever-changing world, being prepared for disasters is crucial. That’s where Virtual Reality (VR) steps in, revolutionizing disaster preparedness and response training. As an expert in the field, I’ve witnessed firsthand the power of VR in simulating realistic disaster scenarios for training purposes.
With VR technology, responders can immerse themselves in various disaster situations, from earthquakes to wildfires, enhancing their decision-making skills and response strategies. The interactive nature of VR not only makes training more engaging but also allows for repetitive practice without real-world consequences.
In this article, I’ll delve into the impact of VR on disaster preparedness and response training, exploring how this innovative technology is shaping the future of emergency readiness.
Overview of VR in Disaster Preparedness and Response Training
Virtual Reality (VR) has transformed the landscape of disaster preparedness and response training. As an expert in this field, I acknowledge the pivotal role that VR technology plays in simulating realistic disaster scenarios for training purposes.
Responders can immerse themselves in various disaster situations, honing their decision-making skills and response strategies effectively. The interactive nature of VR training fosters engagement and enables repetitive practice without real-world consequences.
This innovative technology revolutionizes the way emergency readiness is approached, offering a dynamic and immersive learning experience for responders. VR in disaster preparedness and response training is reshaping traditional training methods, ensuring that responders are better equipped to handle real-life scenarios efficiently.
Advantages of Implementing VR
Virtual Reality (VR) offers numerous advantages when incorporated into disaster preparedness and response training. It provides a level of realism that is unparalleled, making training scenarios incredibly lifelike and immersive.
Realistic Simulation
Incorporating VR technology into disaster preparedness training allows me to experience realistic simulations of various emergency scenarios. These simulations are designed to mimic real-life disasters, providing me with a practical learning environment that closely resembles what I might encounter in the field.
The immersive nature of these simulations helps me develop critical thinking skills and test different response strategies in a safe and controlled setting.
Cost-Effectiveness
Utilizing VR for disaster preparedness training can be a cost-effective solution in the long run. While the initial setup costs may be higher compared to traditional training methods, VR eliminates the need for expensive physical props, travel expenses, and other logistical costs associated with hands-on training.
Additionally, VR simulations can be repeated multiple times without incurring extra expenses, allowing me to practice responses to various scenarios without any additional financial burden. This cost-efficient approach ensures that training remains accessible and affordable while maximizing learning effectiveness.
Challenges Faced in VR Integration
When considering the integration of Virtual Reality (VR) in disaster preparedness and response training, some technology limitations may arise. Addressing these challenges is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of VR applications in such critical scenarios.
Technology Limitations
- Technical Glitches and Malfunctions: Issues such as system errors and hardware failures can disrupt training sessions, affecting the realism and effectiveness of disaster preparedness simulations.
- System Stability and Reliability: Ensuring that VR systems are stable and reliable is crucial for maintaining an immersive and uninterrupted training experience, essential for realistic scenario simulations.
Hardware and Software Compatibility Issues
In my experience, another common challenge is the compatibility between different VR hardware and software components. Mismatched technologies can lead to compatibility issues, affecting the overall performance and user experience during training exercises.
It’s essential to optimize hardware and software configurations to enhance interoperability and seamless operation.
Connectivity and Bandwidth Constraints
I’ve noticed that connectivity and bandwidth constraints can pose significant challenges in VR integration for disaster preparedness training. Limited network capabilities or slow internet speeds can impact the real-time communication and collaboration features crucial for effective response simulations.
Overcoming these constraints requires robust network infrastructure and efficient data transmission protocols.
Training Content Development Complexity
From my observations, developing engaging and realistic training content for VR environments can be complex and time-consuming. Creating interactive scenarios that accurately reflect diverse disaster situations requires specialized skills and resources.
Streamlining the content development process and integrating feedback loops for continuous improvement are essential in addressing this challenge.
User Acceptance and Adaptation
In my view, achieving user acceptance and adaptation to VR technology poses a challenge in disaster preparedness training. Some responders may be unfamiliar or uncomfortable with immersive technologies, leading to resistance or difficulties in navigating VR training platforms.
Providing comprehensive training and support to enhance user proficiency and confidence is essential for successful VR integration.
Maintenance and Upkeep Requirements
Based on my experience, maintaining VR equipment and software solutions involves recurring costs and technical expertise. Regular maintenance activities, software updates, and hardware upgrades are essential to ensure optimal performance and usability of VR systems in disaster preparedness training.
Establishing long-term maintenance plans and partnerships with reliable vendors can help mitigate this challenge.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
I’ve encountered concerns regarding data security and privacy in VR integration for disaster preparedness training. Safeguarding sensitive information, protecting user identities, and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations are critical considerations.
Implementing robust encryption protocols, access controls, and privacy policies is essential to address these security challenges effectively.
Best Practices for VR Implementation
In implementing VR for disaster preparedness and response training, several best practices can enhance the effectiveness of the training and ensure seamless integration into existing protocols. I’ll outline key strategies to optimize the utilization of VR technology in preparing responders for real-life emergency situations:
1. Thorough Needs Assessment:
Before diving into VR implementation, it’s essential to conduct a comprehensive needs assessment to identify specific training gaps and requirements. Understanding the precise needs of responders allows for tailored VR scenario development that directly addresses the challenges they may encounter during disasters.
2. Engaging Content Development:
Creating engaging and realistic VR training content is crucial for effective learning outcomes. Develop scenarios that mirror real-life disaster situations, incorporating interactivity and decision-making elements to enhance critical thinking skills.
Engaging content ensures that responders are fully immersed in the training experience.
3. User Training and Familiarization:
Providing adequate training and familiarization sessions for users is key to successful VR implementation. Ensuring that responders are comfortable with operating VR equipment and navigating through scenarios helps optimize the learning experience.
Regular practice sessions can boost user confidence and proficiency in using VR technology.
4. Continuous Feedback and Improvement:
Encouraging feedback from users and trainers allows for continuous improvement of VR training programs. Collecting insights on user experiences, challenges faced, and areas for enhancement helps refine the VR simulations and tailor them to meet the evolving needs of responders.
Continuous feedback loops enhance the effectiveness of VR training over time.
5. Integration with Overall Training Framework:
Integrating VR training into the overall disaster preparedness framework is essential for seamless implementation. Aligning VR exercises with existing training modules and protocols ensures consistency in learning objectives and reinforces skills learned through traditional training methods.
VR should complement and enhance, rather than replace, conventional training approaches.
6. Regular Maintenance and Updates:
Maintaining VR equipment and software regularly is crucial to prevent technical glitches and ensure smooth operation during training sessions. Updates to VR software should be implemented promptly to incorporate new features, enhance user experience, and address any security vulnerabilities.
Routine maintenance safeguards the reliability and functionality of VR systems.
By following these best practices, organizations can maximize the benefits of VR technology in disaster preparedness and response training, equipping responders with the necessary skills to effectively mitigate crisis situations and save lives.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Exploring case studies and success stories showcasing the integration of Virtual Reality (VR) in disaster preparedness and response training provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of this technology.
Sharing instances of organizations that have successfully adopted VR for training purposes in emergency response can illustrate the practical benefits and outcomes achieved.
Let’s delve into specific examples that demonstrate the impact of VR in enhancing the skills and readiness of responders to effectively handle crisis situations.