As a tech enthusiast always on the lookout for cutting-edge tools, exploring the realm of Augmented Reality (AR) hardware for professional applications is both thrilling and enlightening. In this article, I delve into the intricate world of AR hardware designed specifically for professional use, uncovering the latest advancements and practical implications for various industries.
From innovative headsets to sophisticated smart glasses, the evolution of AR hardware is reshaping how professionals approach tasks and enhance productivity.
Navigating through the complexities of AR hardware can be a daunting task, but understanding its potential impact is crucial in today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape. Join me as we embark on a detailed exploration of the features, benefits, and real-world applications of AR hardware tailored for professionals across diverse sectors.
Let’s unravel the mysteries behind these futuristic devices and unlock the possibilities they offer for revolutionizing the way we work.
Overview of AR Hardware for Professional Use
Augmented Reality (AR) hardware tailored for professional applications represents a pivotal advancement in technology, revolutionizing how industries operate. As a tech enthusiast, I delve into the realm of AR hardware spanning from cutting-edge headsets to innovative smart glasses to uncover their transformative potential across various sectors.
In today’s fast-paced technological landscape, understanding the profound impact of AR hardware is essential for professionals aiming to boost efficiency and revolutionize workflow processes. Let’s delve deeper into the intricacies of AR hardware and explore their features, benefits, and practical applications in diverse industries.
Types of AR Hardware
When it comes to AR hardware for professional use, there are mainly two categories that play a significant role: Head-Mounted Displays (HMDs) and Smart Glasses. Let’s take a closer look at each of these types to understand their functionalities in different professional settings.
Head-Mounted Displays (HMDs)
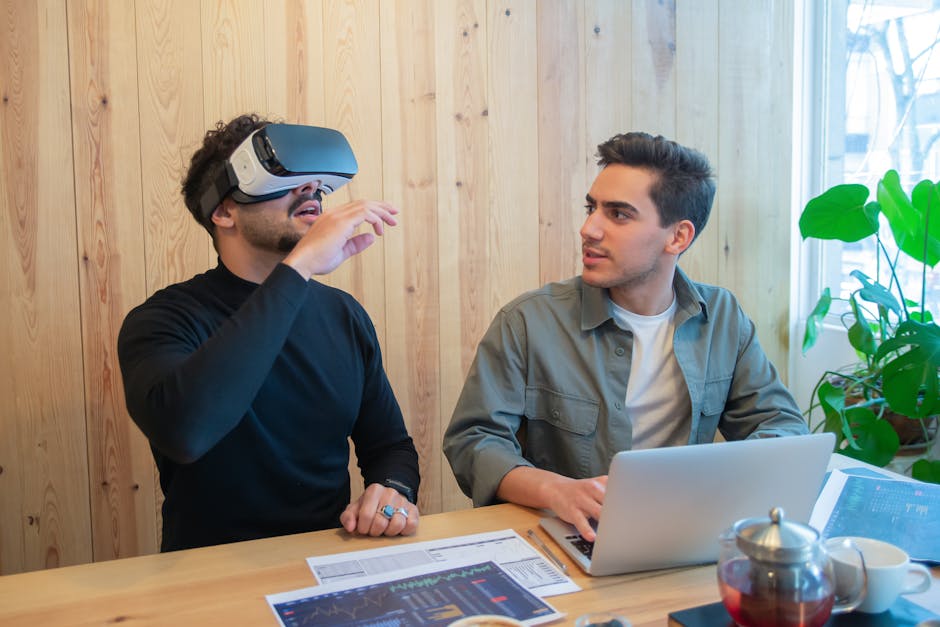
HMDs are a type of AR hardware worn on the user’s head that combines physical reality with virtual elements. They offer immersive experiences by overlaying digital information onto the user’s view of the real world. Professionals across various industries use HMDs to visualize complex data, enhance training simulations, and improve remote collaboration.
Whether it’s for design visualization in architecture or hands-free guidance in manufacturing, HMDs are revolutionizing how professionals interact with information.
Smart Glasses
Smart Glasses are lightweight, wearable devices that display digital information directly onto the user’s field of view. Unlike traditional eyewear, Smart Glasses have integrated displays that can show real-time data, notifications, and instructions without obstructing the user’s vision.
In professional settings, Smart Glasses are used for hands-free access to manuals, AR-guided maintenance tasks, and real-time communication. From field service technicians to healthcare professionals, Smart Glasses provide a seamless way to access critical information while staying focused on the task at hand.
Considerations When Choosing AR Hardware
When selecting AR hardware for professional use, it’s important to assess several key factors to ensure optimal performance and usability in your specific industry context. Here are some essential considerations to keep in mind:
- Compatibility: Make sure the AR hardware you choose is compatible with the software applications and systems used in your work environment. Compatibility issues can hinder seamless integration and limit the functionality of the AR device.
- Comfort and Ergonomics: Prioritize the comfort and ergonomics of the AR hardware, especially if it will be worn for extended periods. Lightweight, properly fitting devices are crucial to prevent discomfort and fatigue during prolonged use.
- Field of View: Consider the field of view offered by the AR hardware, as it directly impacts the user’s ability to interact with augmented content. A wider field of view enhances immersion and allows for better visualization of digital overlays in the real world.
- Battery Life: Evaluate the battery life of the AR hardware, particularly if it will be used for long work sessions or in the field where access to charging may be limited. Longer battery life ensures uninterrupted usage and productivity.
- Durability and Reliability: Assess the durability and reliability of the AR device, especially if it will be used in demanding or rugged environments. Opt for hardware that can withstand challenging conditions to minimize disruptions in workflow.
- Integration Capabilities: Check the integration capabilities of the AR hardware with existing IT infrastructure and software systems. Seamless integration facilitates data exchange and ensures smooth collaboration with other digital tools.
- Security Features: Prioritize AR hardware with robust security features to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. Security vulnerabilities in AR devices can pose significant risks to business operations and confidential information.
By carefully considering these factors when choosing AR hardware for professional use, you can select a device that aligns with your specific requirements and enhances your workflow efficiency effectively.
Challenges Faced with AR Hardware Adoption
Exploring the realm of AR hardware tailored for professional applications has showcased its transformative impact across industries. Cutting-edge Head-Mounted Displays (HMDs) and Smart Glasses have revolutionized workflows and boosted productivity by offering immersive experiences and hands-free access to real-time information.
When considering the adoption of AR hardware for professional use, several challenges may arise, including:
- Integration Complexity: Integrating AR hardware with existing software systems can be complex and time-consuming. It requires seamless compatibility and synchronization to ensure a smooth workflow transition.
- Training and Skill Development: Professionals may need training to effectively utilize AR hardware and maximize its benefits. Skill development programs are essential to ensure users can leverage the hardware for improved productivity.
- Cost Implications: The initial investment and ongoing costs associated with AR hardware adoption can be significant. Organizations need to evaluate the ROI carefully to justify the expenses.
- Interoperability with IT Infrastructure: Ensuring AR hardware can integrate seamlessly with the organization’s IT infrastructure is crucial. Compatibility issues may arise, leading to additional complexities during deployment.
- Security Concerns: Safeguarding sensitive data is paramount when using AR hardware in professional settings. Robust security measures must be implemented to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- User Acceptance and Adoption: Encouraging user acceptance and adoption of AR hardware among professionals may pose a challenge. Overcoming resistance to change and ensuring user buy-in is essential for successful implementation.
By addressing these challenges proactively and implementing strategies to mitigate potential obstacles, professionals can successfully navigate the complexities associated with AR hardware adoption for professional use.